A Phadebas® tablet consists of homogeneously interlinked starch polymers, taking the form of globular microspheres of defined size. These Bio-Degradable Starch Microspheres (DSM)are insoluble in water. To the DSMs, a blue dye is covalently bound. When the dye is bound to the microsphere, it remains water insoluble. However, in the presence of alpha Amylase, the DSM is degraded at a speed proportional to the alpha Amylase activity, and the blue dye is liberated. Due to the cross-linkages and the large blue dye, no other enzyme can act upon the substrate. Hence, Phadebas is specific for alpha amylase. The free dye molecule is water soluble and its concentration measurable at 620 nm. Using a fixed assay time, the absorbance reading gives the solution’s Amylase activity, through the standard curve supplied with each kit.
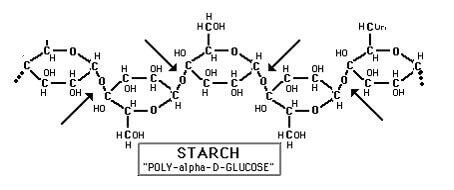
Part of a starch chain with arrows indicating points of action for the alpha amylase enzyme.
In the qualitative Phadebas Forensic Press Test, the diffusion of the liberated dye molecules is used to indicate the likely presence of salivary Amylase. In Phadebas Honey Diastase Test, the reactivity is controlled in a manner that ensures exact reproducibility between batches.
In semi-quantitative assays, such as Analis’s Isoamyl assay, the blue dye is used for visual detection. After electrophoretic separation of the various subclasses of salivary and pancreatic Amylases, Phadebas® tablets are dissolved on top of the gel. Where Amylase activity degrades the DMSs, the free dye diffuses into the gel, while non-degraded DSMs (and dye) is washed away. The remaining colored spots reveal the Amylase pattern, for diagnostic purposes.
3D model of salivary alpha-amylase enzyme.
For questions regarding the Phadebas assay, amylase testing and starch; please contact us at info@phadebas.com.
About Amylase
Amylase is an enzyme that is present in many shapes. It can be divided in three categories; alpha-, beta- and gamma-amylase. All three types are glucoside hydrolases and take part in the process of starch degradation by acting on α-1,4-glycosidic bonds to create short-chain sugars.
Amylase is used in for instance;
- Brewing and fermentation;
- Textile industry for designing textiles;
- Detergents in the laundry industry;
- Paper industry for sizing;
- Food industry for removal of starch, preparation of syrups etc.
α-amylase
α-amylase is an enzyme found in various forms in the nature. Two isoforms are found in the human body; salivary alpha amylase and pancreatitic alpha amylase. Both variants take part in the digestion of starch. α-amylase is also present in fungi, bacteria and different plants. As an example, α-amylase is produced during germination of seeds.
Unlike other amylases, α-amylase can hydrolyse alpha-bonds in starch at random locations on the polymer chain, thereby making it a faster enzyme compared to other amylases. The end products are maltos and glucose from amylopectin and maltos and maltotriose from amylose.
β-amylase
β-amylase is an enzyme found in fungi, bacteria and plants but not in humans. Unlike α-amylase, β-amylase can only degrade starch from the non-reducing end of the polymer chain by hydrolysis of the second α-1,4 glycosidic bond. The end product is thus maltose, i.e. two glucose units. As α-amylase, β-amylase is present in seeds and is used in a variety of applications, for instance malting. A high volume application is the production of high maltose syrups.
γ-amylase
γ-amylase is an enzyme that is less frequently used in the industry. It degrades starch from the non-reducing end by hydrolysing the last α(1-4)glycosidic linkage, thereby yielding one glucose unit. In addition, it hydrolyse α(1-6) glycosidic linkages. The enzyme has a lower ph optimum compared to other amylases.
